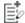Flat pigmented macules on sun-damaged skin of the head/neck: junctional nevus, atypical lentiginous nevus, or melanoma in situ?
Zalaudek I, Cota C, Ferrara G, Moscarella E, Guitera P, Longo C, Piana S, Argenziano G., Clin Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;32(1):88-93. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.05.029.
The clinical recognition of lentigo maligna (LM) in the mottled chronic sun-damaged skin can be challenging, because it shares many clinical features with other pigmented macules that commonly arise on sun-damaged skin. These include solar lentigo, flat seborrheic keratosis, and pigmented actinic keratosis, but almost never "nevus." The reason nevus is not included in the differential diagnosis of LM can be explained by the fact that the stereotypical appearance of a facial nevus differs remarkably from that of an LM. Facial nevi in adults are usually nodular, dome-shaped, well-defined, and hypopigmented (i.e., intradermal nevus of the Miescher type), whereas LM typically appears as a flat, ill-defined, and pigmented macule. Although this concept based on clinical observations sounds reasonable, clinicians apply it often only unconsciously and accept a given histopathologic diagnosis of a "junctional or lentiginous nevus" of a flat pigmented facial macule without the necessary criticism about its clinicopathologic validity.


 back to overview
back to overview